The connection between oxalates and autism is a subject of ongoing research. Some theories suggest that children with autism may have higher levels of oxalates in their bodies due to gut dysbiosis or metabolic differences. Elevated oxalate levels could potentially contribute to the gastrointestinal issues commonly seen in individuals with autism, such as diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain.
Read MoreProteins are the building blocks of life, and their importance extends across multiple aspects of health, including the immune system, blood sugar regulation, behavior, growth, and muscle development. This blog delves into how proteins benefit children with autism in these key areas and highlights the best sources of protein to include in their diets.
Read MoreSimple carbohydrates, such as those found in sugary cereals, donuts, and pop tarts, are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. These spikes are often followed by a rapid decline, or "crash," as insulin works to remove excess glucose from the bloodstream. This cycle of spikes and crashes can significantly affect mood, behavior, and cognitive function. For individuals with autism and ADHD, who may already struggle with emotional regulation and focus, these fluctuations can exacerbate symptoms and lead to challenging behaviors.
Read MoreOngoing research has shed light on various biological and nutritional factors that may influence its development and progression of autism. Among these factors, oxytocin and cholesterol deficiencies have garnered significant attention.
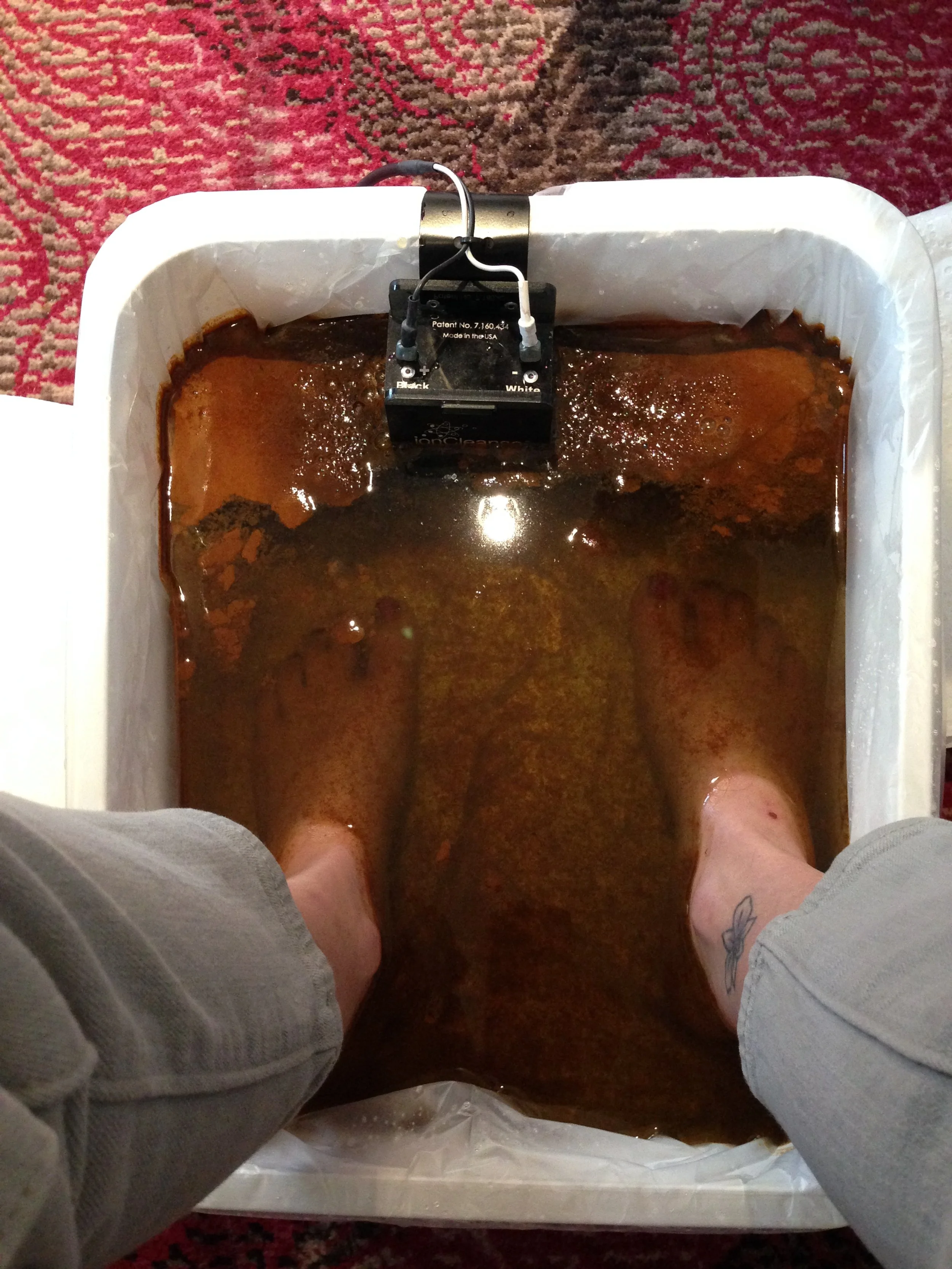
Read MoreWhile there are numerous detox methods available, one that has garnered attention for its gentle yet effective approach is the IonCleanse foot bath by A Major Difference (AMD). This method offers a non-invasive and soothing way to support the body's natural detoxification processes, making it particularly suitable for individuals with autism.
Read MoreWhile the core characteristics of autism include challenges in social communication and repetitive behaviors, it is important to recognize that many individuals with autism also experience a range of comorbid conditions. These comorbidities can significantly impact quality of life and include obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), anxiety, sleep disorders, and gastrointestinal (GI) issues such as reflux, constipation, celiac disease, eosinophilic esophagitis (EOE), and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD).
Read MoreAmong the various nutrients that play a significant role in autism, folate stands out due to its profound impact on neurological development and function. Folate, a water-soluble B vitamin (B9), is essential for DNA synthesis, repair, and methylation, which are critical processes for cell division and proper functioning of the nervous system. Folate is naturally found in leafy greens, legumes, and certain fruits. The synthetic form, folic acid, is commonly added to fortified foods and supplements.
Read MoreThe GAPS diet, or Gut and Psychology Syndrome diet, is a nutritional protocol designed by Dr. Natasha Campbell-McBride. This diet aims to heal the gut lining and restore healthy gut flora, which is believed to influence neurological conditions such as autism, ADHD, dyslexia, dyspraxia, and depression. Dr. Campbell-McBride developed the GAPS diet based on the understanding that a compromised gut can lead to toxins entering the bloodstream and affecting brain function, a concept often referred to as "leaky gut syndrome."
Read MoreChildren with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) often experience a range of feeding challenges that can significantly impact their nutrition, growth, and overall health. As a dietitian nutritionist specializing in autism, it is essential to understand the multifaceted nature of these feeding issues to provide effective support and intervention. This article explores the reasons behind feeding challenges in children with autism, examining sensory, behavioral, and physiological factors, and offers strategies to address these issues.
Read MoreIn recent years, sulforaphane, a compound found in cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, has emerged as a potential therapeutic agent for autism. This article delves into the latest research on sulforaphane and its impact on autism, exploring the benefits and improvements it may offer.
Read MoreFor children with autism, food aversions and sensory sensitivities can make meal planning a challenge. However, incorporating a variety of textures and flavors can make a significant difference. Strawberries are a versatile and nutrient-rich fruit that can be enjoyed in several ways. Here, I present four delightful strawberry recipes: fresh cut in cute shapes, frozen, baked, and dried. Each method offers a unique sensory experience that may appeal to even the pickiest of eaters.
Read MoreThis delicious snack is filled with great nutrients and does not contain gluten, dairy, soy or any artificial food dyes or additives.
Read MoreGlutathione, often dubbed the "master antioxidant," plays a crucial role in the body's detoxification processes and overall health. As an autism dietitian nutritionist, understanding the significance of glutathione is paramount, especially given its potential implications in managing autism spectrum disorder (ASD). This article delves into the science behind glutathione, its functions, relevance to autism, dietary sources, factors that deplete it, and the most effective forms of supplementation.
Read MoreThe differences between grass-fed beef and conventional farm factory beef are substantial, impacting nutrition, the environment, animal welfare, and even taste. Grass-fed beef offers a superior nutritional profile, including higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, CLA, vitamins, and minerals, making it a healthier choice for those seeking optimal health benefits.
Read MoreAggression in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) can manifest in various forms, presenting significant challenges for both the individual and their caregivers. While autism itself is characterized by differences in social communication and behavior, aggression often arises from underlying medical issues. It's crucial to recognize and address these medical causes to better support individuals with autism and improve their quality of life. Among the potential medical contributors to aggression in autism are various pain-inducing conditions, gastrointestinal (GI) issues, chronic infections, medication side effects, hormonal imbalances, and nutritional deficiencies.
Read MoreOver the years, researchers have delved into various factors contributing to the etiology of ASD, and evidence suggests this development is multifactoral and one potential link is with vitamin D deficiency.
Read MoreWhile these conditions present unique hurdles, evidence suggests that dietary interventions can play a significant role in improving attention and focus in children with autism and ADHD. As a specialized autism dietitian nutritionist, I advocate for a holistic approach that incorporates dietary changes and targeted nutrient supplementation to support cognitive function and overall well-being.
Read MoreReflux is a common condition characterized by the backward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus, causing discomfort and potential complications. While reflux can affect individuals of all ages, children with autism seem to have a higher prevalence of this condition.
Read MoreFor children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), ensuring optimal magnesium levels is of paramount importance. Magnesium supplementation and therapies like Epsom salt baths offer promising avenues for addressing various challenges faced by children with autism, ranging from calming effects to alleviating sleep disturbances, constipation, headaches, and muscle pain.
Read MoreMany families have found that eliminating certain foods, such as gluten, casein, soy, and additives/food colorings, can have a positive impact on their children's symptoms. Here are some quick and easy, nutritious recipes that are free of these common triggers and are sure to be favorites among kids.
Read More