Is ADHD Medication the Right Choice for Your Child?
Ritalin
Ritalin and Adderall are the two most common medications prescribed for ADHD. While they may be effective at controlling unwarranted behaviors and improving concentration, there are many side effects that come along with it. There is a time and place for these medications, though, it is important to know possible side effects and there are more natural and very effective alternatives.
Introduction of Ritalin:
One of the most common central nervous system stimulants prescribed in children over age of 6
Schedule II Narcotic
Same classification as morphine, methamphetamines and codeine
High potential for abuse
S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) reports that studies show that Ritalin is more potent than cocaine and effects the brain in the same way as cocaine does
Stimulants are most common treatment of ADHD and are also being used as a treatment for narcolepsy
According to the National Center for Health Statistics Data Brief no. 42, from 2007 – 2008, “The most commonly used types of prescription drugs in the United States by age were: ….central nervous system stimulants for adolescents aged 12–19.”
The prevalence of children 4-17 years of age taking ADHD medication increased from 4.8% in 2007 to 6.1% in 2011
More than 17 million children worldwide prescribed psychiatric medicines
How does Ritalin work?
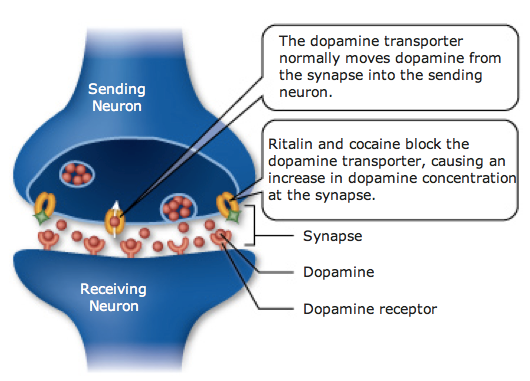
Ritalin increases dopamine levels in the brain
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter which plays a critical role in moods, behaviors and motivation
Ritalin blocks a protein responsible for transporting dopamine
Affects chemicals and nerves which contribute to hyperactivity and impulse control
“Methylphenidate blocks dopamine uptake in central adrenergic neurons by blocking dopamine transport or carrier proteins. Methylphenidate acts at the brain stem arousal system and the cerebral cortex and causes increased sympathomimetic activity in the central nervous system. Alteration of serotonergic pathways via changes in dopamine transport may result.”
It is believed that those with ADHD may have more of these dopamine transporters than others.
Ritalin as a Recreational Drug:
DEA has received reports of college students using Ritalin to help them study for all-night study sessions
Many also admittedly use Ritalin as a “party drug”
One survey of students at a public liberal arts college found that “over 50% of survey participants knew other students who had used Ritalin for fun, 16% had used it themselves, and nearly 13% reported their own use included snorting the drug.”
Chronic heavy use can lead to physical dependence-- withdrawal symptoms include exhaustion and severe emotional depression
Ritalin’s dependence can cause cravings for the drug and panic if it becomes unavailable
Nutrients Depleted from Ritalin use and Symptoms Associated:
Some children are at risk of serious growth decrement when treated with MPH” (methylphenidate/Ritalin)
Nutrient intake and growth of children taking methylphenidate should be monitored very closely
Calcium/Magnesium ratio significantly lower after 3 weeks of treatment with methylphenidate
“the decrease in the ratio may be relevant to side effects and treatment resistance associated with stimulant use.”
Significantly depletes dopamine and causes cell death in olfactory bulb
Olfactory bulb is part of the limbic system and is involved in motivation, emotions and memory
May be related to the depressive symptoms associated with amphetamine withdrawal
Caffeine can enhance side effects of Ritalin so it is recommended to limit caffeine to small quantities
Alcohol should be avoided as it may increase nervous system side effects such as drowsiness, anxiety, depression, and seizures
When Alcohol is combined with methylphenidate, a metabolite known as ethylphenidate is produced, which can be fatal in some individuals.
There are many natural alternatives to treating ADHD which also improve optimal health status. Looking for specific food intolerance’s and micronutrient deficiencies is especially helpful. Other improvements can be seen with:
Adding Omega 3’s
Nixing Food Additives
Vitamin B6 and Magnesium
Exercise
Studies have shown significant reduction in ADHD symptoms and overall health by optimizing diet and lifestyle.
Amphetamines.com, Facts and Statistics on Amphetamine Abuse, http://amphetamines.com/facts/facts-and-statistics-on-amphetamine-abuse/ Accessed December 2, 2015
Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA), http://www.dea.gov/druginfo/ds.shtml Accessed December 2, 2015
Drug-Induced Nutrient Depletion Handbook, by Ross Pelton, R.PH., PH.D; James B. LaValle, R.Ph., and Ernest B. Hawkins, R.Ph., M.S. (Lexi-Comp, 2001]
Atianjoh, Fidelis E. et al. 'Amphetamine Causes Dopamine Depletion And Cell Death In The Mouse Olfactory Bulb'. European Journal of Pharmacology 589.1-3 (2008): 94-97. Web. 2 Dec. 2015.
Schmidt, ME., et.al, Effect of dextroamphetamine and methylphenidate on calcium and magnesium concentration in hyperactive boys., Psychiatry Res. 1994 Nov;54(2):199-210
Garfinkel BD, et al. 'Individual Responses To Methylphenidate And Caffeine In Children With Minimal Brain Dysfunction, Canadian Medical Assoc Journal. - Pubmed - NCBI'. Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. N.p., 2015. Web. 3 Dec. 2015.
Krueger J, et al. 'First Detection Of Ethylphenidate In Human Fatalities After Ethylphenidate Intake., Forensic Science Int. - Pubmed - NCBI'. Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. N.p., 2015. Web. 3 Dec. 2015.
Zhu, Hao-Jie, Kennerly S. Patrick, and John S. Markowitz. 'Enantiospecific Determination Of Dl-Methylphenidate And Dl-Ethylphenidate In Plasma By Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Application To Human Ethanol Interactions'. Journal of Chromatography B 879.11-12 (2011): 783-788. Web. 3 Dec. 2015.
Dolina, S. et al. 'Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) As A Pyridoxine-Dependent Condition: Urinary Diagnostic Biomarkers'. Medical Hypotheses 82.1 (2014): 111-116. Web. 2 Dec. 2015.
B L Hungund, B G Winsberg. 'Pharmacokinetics Of Methylphenidate In Hyperkinetic Children.'. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 8.6 (1979): 571. Web. 2 Dec. 2015.
DrugBank, Methylphenidate, http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00422
Neuropsychopharmacology, ADHD and attention networks, (Image), http://www.nature.com/npp/journal/v35/n1/fig_tab/npp2009120f2.html#figure-title
Center for Substance Abuse Research, Ritalin, http://www.cesar.umd.edu/cesar/drugs/ritalin.asp Accessed December 2, 2015
Holtkamp, K., et.al, Methylphenidate-related growth impairment, J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2002 Spring;12(1):55-61.
Schmidt, ME., et.al, Effect of dextroamphetamine and methylphenidate on calcium and magnesium concentration in hyperactive boys., Psychiatry Res. 1994 Nov;54(2):199-210
Atianjoh, Fidelis E. et al. 'Amphetamine Causes Dopamine Depletion And Cell Death In The Mouse Olfactory Bulb'. European Journal of Pharmacology 589.1-3 (2008): 94-97. Web. 2 Dec. 2015.